Awakened
Posthumanism, often misconstrued as rejecting humanity, is more accurately a critical examination of human exceptionalism. It challenges the belief in humans as autonomous entities standing apart from intricate networks of relations.
Posthumanism can unexpectedly emerge within humanistic perspectives that grapple with the limitations of understanding humanity and endeavor to transcend them.
Medium
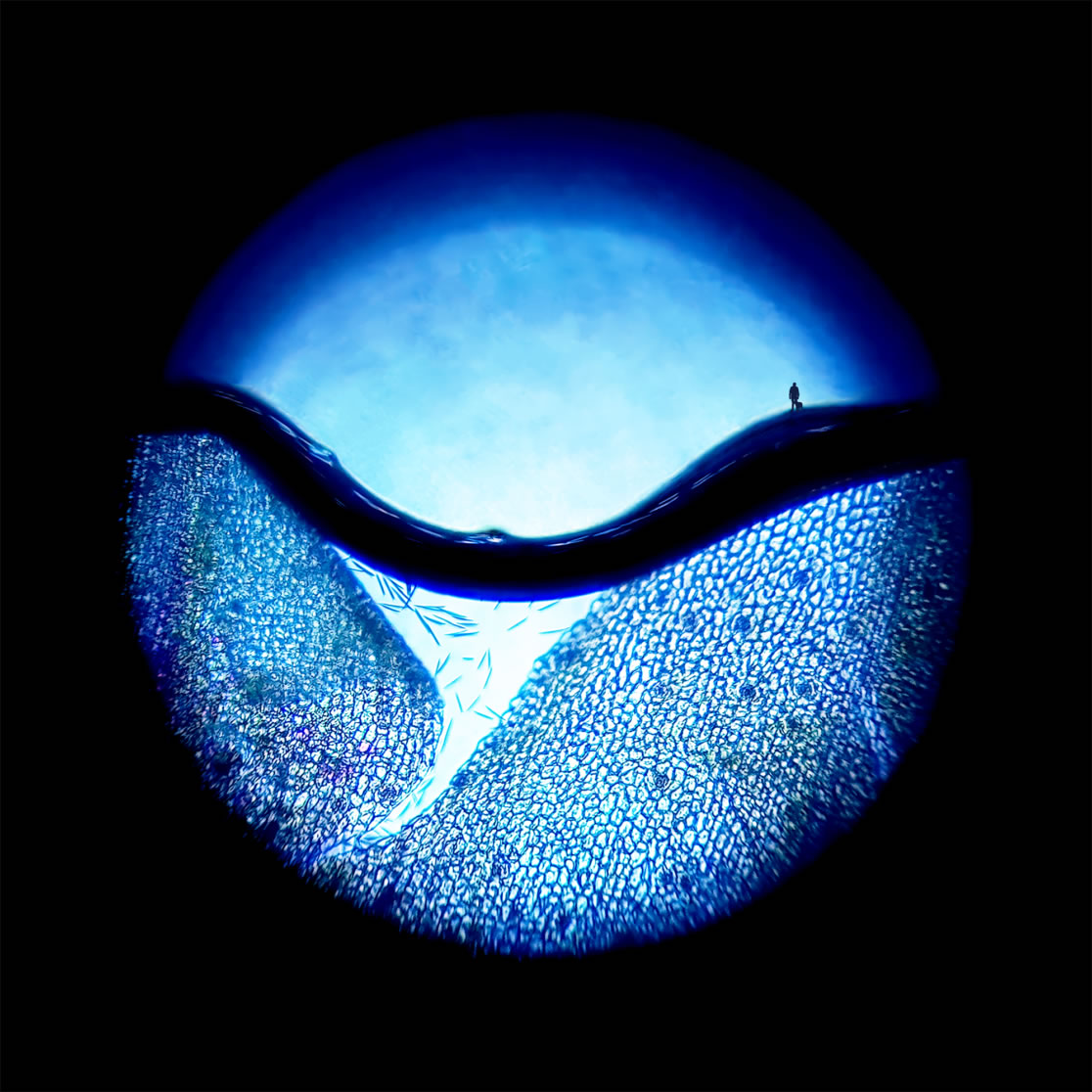
Canine olfactory sourced biota with digital overlays.
Image type
Digital C-Type print, flush-mounted on 3mm Alupanel
Dimensions
150 x 150 x 3 mm
Critical context
“It is not simply a matter of new forms of visuality—this calls for the kind of recalibration, redistribution, and displacement of the relationship between meaning and the entire sensorium of living beings, in which visuality itself (as the human sensory apparatus par excellence) is now thoroughly decentered and subjected to a rather different kind of logic.” (Wolfe 2021, 88)In the context of animals and the environment, posthumanism challenges the anthropocentric view that places humans as superior and detached from nature. It explores interconnectedness, recognizing the agency and value of non-human entities. Posthumanist perspectives emphasize ethical considerations, advocating for a more inclusive and symbiotic relationship between humans, animals, and the environment, challenging traditional hierarchies and fostering a collaborative approach to human-animal-environmental well-being.
Main explorative points:
1. Non-Anthropocentric Focus:
- Challenges human-centric views.
- Rejects the idea of human superiority over animals and the environment.
Interconnectedness:
- Emphasizes the interconnected web of relations between humans, animals, and the environment.
- Acknowledges the agency and intrinsic value of non-human entities.
Ethical Considerations:
- Advocates for ethical treatment of animals and responsible environmental practices.
- Questions exploitative and harmful approaches driven by anthropocentric perspectives.
Inclusive Relationships:
- Fosters a more inclusive, symbiotic relationship between humans and the natural world.
- Encourages collaboration and coexistence rather than domination.
Holistic Ecological Approach:
- Challenges traditional hierarchies in ecological thinking.
- Promotes a holistic approach to environmental well-being, recognizing the interconnectedness of all living entities.
“When applied to assistance animals, posthumanism challenges traditional hierarchies, emphasizes the agency and subjectivity of animals, explores the ethical implications of trans-species interventions, and encourages a more inclusive consideration of the diverse symbiotic relationships that are occuring in the 21st century.”
Citations:
Chandler, Eliza, Katie Aubrecht, Esther Ignagni, and Carla Rice. 2021. “Cripistemologies of Disability Arts and Culture: Reflections on the Cripping the Arts Symposium (Editors’ Introduction).” Studies in Social Justice 15 (2): 170-179. https://www.proquest.com/scholarly-journals/cripistemologies-disability-arts-culture/docview/2538052982/se-2.
Landgraf, Edgar, Trop, Gabriel, and Weatherby, Leif, eds. 2018. Posthumanism in the Age of Humanism : Mind, Matter, and the Life Sciences after Kant. New York: Bloomsbury Academic & Professional. Accessed February 5, 2024. ProQuest Ebook Central. http://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/curtin/detail.action?docID=5515143
Wolfe, Cary. 2021. Art and Posthumanism (Art After Nature) (p. 86). University of Minnesota Press. Personal Kindle Edition.
Wolfe, C. 2010. What is posthumanism? Minnesota: University of Minnesota Press.